Bitumen is typically derived from crude oil through a refining process called distillation. It is a by-product of crude oil refining, especially during the production of lighter petroleum products like gasoline and diesel. There are two primary types of bitumen production:
Natural Bitumen: This is found in natural deposits, such as tar sands or oil sands, where bitumen is extracted directly from the earth.
Refined Bitumen: This is produced from crude oil through heavy distillation. After the lighter fractions (like gasoline and diesel) are removed, bitumen remains as a thick, heavy residue.
Uses of Bitumen
Road Construction (Asphalt):
Paving Roads: The most common use of bitumen is in road construction, where it is mixed with aggregates (such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone) to form asphalt. The bitumen acts as a binder that holds the aggregate together, creating durable and flexible road surfaces.
Durability: Bitumen-based asphalt is resistant to water, weathering, and wear, making it ideal for roads, highways, and airstrips.
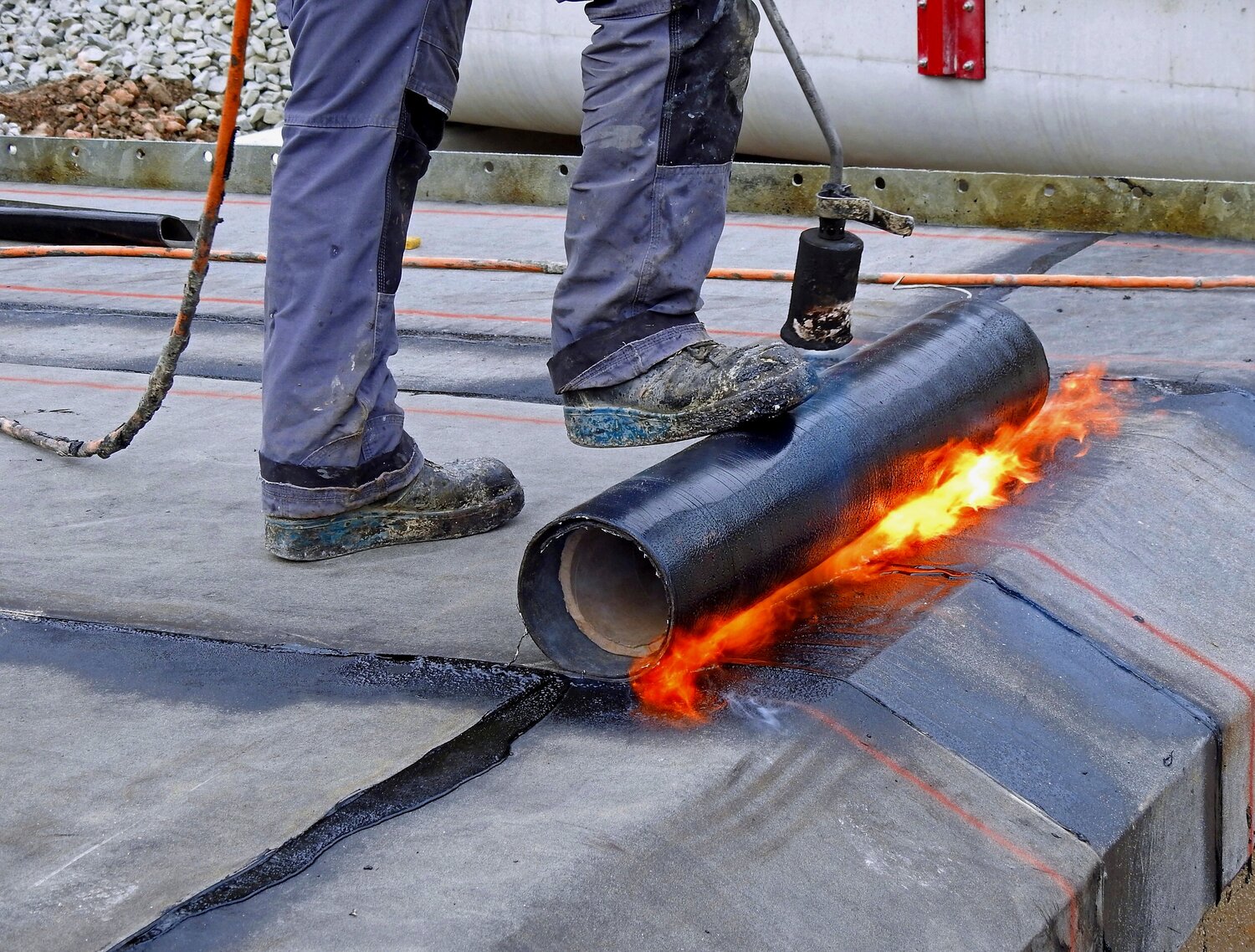
Roofing:
Waterproofing: Bitumen is widely used in roofing materials such as bituminous roofing membranes and shingles. It provides a waterproof barrier to protect buildings from water ingress, particularly in flat-roofed buildings.
Modified Bitumen: In some applications, bitumen is modified with materials like rubber or plastic to enhance its flexibility and performance at different temperatures.


Waterproofing and Coatings:
Sealing and Protection: Bitumen is also used in products for sealing and waterproofing foundations, basements, and other structures that need to resist water. It is applied as a thick coating to prevent moisture penetration.
Corrosion Protection: Bitumen coatings are used for protecting pipelines and steel structures from corrosion, particularly in underground or marine environments.
Industrial Applications:
Emulsions: Bitumen is mixed with water and surfactants to create bitumen emulsions, which are used in road maintenance, including pothole repair and surface treatments.
Sealants and Adhesives: Bitumen can be processed into various forms, including cold-applied sealants and adhesives for construction and industrial purposes.
Energy Production:
Synthetic Fuels: In some cases, bitumen from oil sands is converted into synthetic crude oil, which can then be refined into gasoline, diesel, and other fuels.
Advantage of Bitumen
- Durability: Bitumen is resistant to weathering, oxidation, and the effects of UV light, making it highly durable in outdoor applications like roads and roofs.
- Water Resistance: It provides an excellent barrier to water, preventing moisture damage to structures and pavements.
- Flexibility: It can be modified to be more flexible or rigid depending on the application, especially in roofing and road construction.
- Cost-Effective: Bitumen is generally a relatively inexpensive material, especially when compared to alternatives like concrete or metal for waterproofing and road construction.